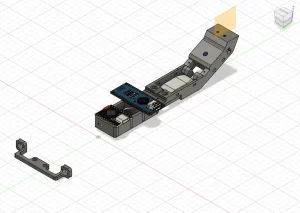
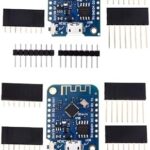
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to make a custom RC Receiver by modifing a WLToys K989 RC Car with a ESP32-C6 Super Mini. This works with most RC cars that use Servo and ESC.
It’s incredibly easy.
Buy the parts needed:
- RC Car Wltoys K989……………………….… Amazon / Banggood / Shopee
- Brushed ESC 10A with brakes ……….… Amazon / Banggood
- ESP32 C6 Super Mini ..………………….… Amazon / Banggood / Shopee
- Thin wires 22 Awg (optional) …….….… Amazon / Banggood
- JST 2 Conectors (optional) .………..….… Amazon / Banggood
Disclosure: These are affiliate links. I earn a little comission if you use my links to buy the parts.
Please use them to help me continue building cool projects.
Step1: Download all the files for this project
I wish everyone made things easy like this.
Step2: 3D Print the supports for the boards
If you have the same car as i do, the Wltoys K989, or one of the similar ones, you can start printing the parts and while waiting for it to finish we can do the other stuff.
See how to assemble on step9.
Step3: Install the ESP32 Board on the Arduino IDE
Download and install the Arduino IDE.
Access the menu File > Preferences.
Insert the URL below at Additional Boards Manager URL’s.
https://espressif.github.io/arduino-esp32/package_esp32_index.json
Arduino IDE will download the ESP32 boards information. Then you’ll be able to select it from the Boards menu.
Step4: Install the necessary libraries on the Arduino IDE
Download these libraries and install them on your Arduino libraries folder.
If you don’t know how, see this guide.
You can search and install IRremote and ArduinoJson directly on the Arduino libraries tab.
The others you must download and install. Restart Arduino IDE after.
Step6: Upload the test code for the RC Car
Press and hold the boot button on the ESP32 board then connect the USB cable to boot in flash mode.
Make sure to select the correct Board: ESP32C6 Dev Module. NOT ESP32 Family Device
To enable the serial monitor, you must enable “USB CDC On Boot”
Step11: Upload the code for the IR Transmitter
Make sure to change the remote control codes to match the car you’re going to use.
IR_transmitter.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "PinDefinitionsAndMore.h" // Define macros for input and output pin etc.
#include <IRremote.hpp>
// default IR_SEND_PIN for ESP32-S3 is pin 3
// default IR_SEND_PIN for ESP32-C6 is pin 3
// default IR_SEND_PIN for Arduino nano is pin 3
#define DELAY_AFTER_SEND 20
uint16_t sAddress = 0x0102;
uint8_t sRepeats = 0;
uint8_t sCommand = 0x11; // car1
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x12;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x13;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x14;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x15;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x16;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x17;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x18;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x19;
// uint8_t sCommand = 0x10; // car10
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
IrSender.begin(); // Start with IR_SEND_PIN -which is defined in PinDefinitionsAndMore.h- as send pin and enable feedback LED at default feedback LED pin
IrSender.enableIROut(38); // Call it with 38 kHz just to initialize the values printed below
disableLEDFeedbackForSend();
}
void loop() {
IrSender.sendNEC(sAddress, sCommand, sRepeats);
delay(DELAY_AFTER_SEND); // delay must be greater than 5 ms (RECORD_GAP_MICROS), otherwise the receiver sees it as one long signal
}
PinDefinitionsAndMore.h
/*
* PinDefinitionsAndMore.h
*
* Contains pin definitions for IRremote examples for various platforms
* as well as definitions for feedback LED and tone() and includes
*
* Copyright (C) 2021-2023 Armin Joachimsmeyer
* armin.joachimsmeyer@gmail.com
*
* This file is part of IRremote https://github.com/Arduino-IRremote/Arduino-IRremote.
*
* Arduino-IRremote is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
* See the GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>.
*
*/
/*
* Pin mapping table for different platforms
*
* Platform IR input IR output Tone Core/Pin schema
* --------------------------------------------------------------
* DEFAULT/AVR 2 3 4 Arduino
* ATtinyX5 0|PB0 4|PB4 3|PB3 ATTinyCore
* ATtiny167 3|PA3 2|PA2 7|PA7 ATTinyCore
* ATtiny167 9|PA3 8|PA2 5|PA7 Digispark original core
* ATtiny84 |PB2 |PA4 |PA3 ATTinyCore
* ATtiny88 3|PD3 4|PD4 9|PB1 ATTinyCore
* ATtiny3217 18|PA1 19|PA2 20|PA3 MegaTinyCore
* ATtiny1604 2 3|PA5 %
* ATtiny816 14|PA1 16|PA3 1|PA5 MegaTinyCore
* ATtiny1614 8|PA1 10|PA3 1|PA5 MegaTinyCore
* SAMD21 3 4 5
* ESP8266 14|D5 12|D6 %
* ESP32 15 4 27
* ESP32-C3 2 3 4
* BluePill PA6 PA7 PA3
* APOLLO3 11 12 5
* RP2040 3|GPIO15 4|GPIO16 5|GPIO17
*/
//#define _IR_MEASURE_TIMING // For debugging purposes.
#if defined(__AVR__)
#if defined(__AVR_ATtiny25__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny45__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny85__) // Digispark board. For use with ATTinyCore.
#include "ATtinySerialOut.hpp" // TX is at pin 2 - Available as Arduino library "ATtinySerialOut". Saves 700 bytes program memory and 70 bytes RAM for ATtinyCore.
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PB0
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PB4 // Pin 2 is serial output with ATtinySerialOut. Pin 1 is internal LED and Pin3 is USB+ with pullup on Digispark board.
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PB3
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN PIN_PB3
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny87__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny167__) // Digispark pro board
#include "ATtinySerialOut.hpp" // Available as Arduino library "ATtinySerialOut"
// For ATtiny167 Pins PB6 and PA3 are usable as interrupt source.
# if defined(ARDUINO_AVR_DIGISPARKPRO)
// For use with Digispark original core
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 9 // PA3 - on Digispark board labeled as pin 9
//#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 14 // PB6 / INT0 is connected to USB+ on DigisparkPro boards
#define IR_SEND_PIN 8 // PA2 - on Digispark board labeled as pin 8
#define TONE_PIN 5 // PA7 - on Digispark board labeled as pin 5
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 10 // PA4
# else
// For use with ATTinyCore
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PA3 // On Digispark board labeled as pin 9 - INT0 is connected to USB+ on DigisparkPro boards
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA2 // On Digispark board labeled as pin 8
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PA7 // On Digispark board labeled as pin 5
# endif
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny84__) // For use with ATTinyCore
#include "ATtinySerialOut.hpp" // Available as Arduino library "ATtinySerialOut". Saves 128 bytes program memory.
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PB2 // INT0
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA4
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PA3
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN PIN_PA5
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny88__) // MH-ET Tiny88 board. For use with ATTinyCore.
#include "ATtinySerialOut.hpp" // Available as Arduino library "ATtinySerialOut". Saves 128 bytes program memory.
// Pin 6 is TX, pin 7 is RX
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PD3 // 3 - INT1
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PD4 // 4
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PB1 // 9
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN PIN_PB0 // 8
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny1616__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny3216__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny3217__) // For use with megaTinyCore
// Tiny Core Dev board
// https://www.tindie.com/products/xkimi/tiny-core-16-dev-board-attiny1616/ - Out of Stock
// https://www.tindie.com/products/xkimi/tiny-core-32-dev-board-attiny3217/ - Out of Stock
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PA1 // use 18 instead of PIN_PA1 for TinyCore32
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA2 // 19
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PA3 // 20
#define APPLICATION_PIN PIN_PA0 // 0
#undef LED_BUILTIN // No LED available on the TinyCore 32 board, take the one on the programming board which is connected to the DAC output
#define LED_BUILTIN PIN_PA6 // use 2 instead of PIN_PA6 for TinyCore32
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny816__) // For use with megaTinyCore
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PA1 // 14
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA1 // 16
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PA5 // 1
#define APPLICATION_PIN PIN_PA4 // 0
#undef LED_BUILTIN // No LED available, take the one which is connected to the DAC output
#define LED_BUILTIN PIN_PB5 // 4
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny1614__) // For use with megaTinyCore
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PA1 // 8
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA3 // 10
#define TONE_PIN PIN_PA5 // 1
#define APPLICATION_PIN PIN_PA4 // 0
# elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny1604__) // For use with megaTinyCore
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PIN_PA6 // 2 - To be compatible with interrupt example, pin 2 is chosen here.
#define IR_SEND_PIN PIN_PA7 // 3
#define APPLICATION_PIN PIN_PB2 // 5
#define tone(...) void() // Define as void, since TCB0_INT_vect is also used by tone()
#define noTone(a) void()
#define TONE_PIN 42 // Dummy for examples using it
# elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1284__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega1284P__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega644__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega324P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega324A__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega324PA__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega164A__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega164P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega32__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega16__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega8535__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega64__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega128__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega1281__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2561__) \
|| defined(__AVR_ATmega8515__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega162__)
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 13
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
# else // Default as for ATmega328 like on Uno, Nano, Leonardo, Teensy 2.0 etc.
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2 // To be compatible with interrupt example, pin 2 is chosen here.
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
# if defined(ARDUINO_AVR_PROMICRO) // Sparkfun Pro Micro is __AVR_ATmega32U4__ but has different external circuit
// We have no built in LED at pin 13 -> reuse RX LED
#undef LED_BUILTIN
#define LED_BUILTIN LED_BUILTIN_RX
# endif
# endif // defined(__AVR_ATtiny25__)...
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_RENESAS_UNO) // Uno R4
// To be compatible with Uno R3.
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
#elif defined(ESP8266)
#define FEEDBACK_LED_IS_ACTIVE_LOW // The LED on my board (D4) is active LOW
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 14 // D5
#define IR_SEND_PIN 12 // D6 - D4/pin 2 is internal LED
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 2 // D4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 13 // D7
#define tone(...) void() // tone() inhibits receive timer
#define noTone(a) void()
#define TONE_PIN 42 // Dummy for examples using it#
#elif defined(ARDUINO_NOLOGO_ESP32C3_SUPER_MINI)
#define FEEDBACK_LED_IS_ACTIVE_LOW // The LED on my board (D8) is active LOW
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 10
#elif defined(CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32C3) || defined(ARDUINO_ESP32C3_DEV)
#define NO_LED_FEEDBACK_CODE // The WS2812 on pin 8 of AI-C3 board crashes if used as receive feedback LED, other I/O pins are working...
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 6
#define IR_SEND_PIN 7
#define TONE_PIN 10
#define APPLICATION_PIN 18
#elif defined(ESP32)
#include <Arduino.h>
// tone() is included in ESP32 core since 2.0.2
#if !defined(ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION_VAL)
#define ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION_VAL(major, minor, patch) 12345678
#endif
#if ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION <= ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION_VAL(2, 0, 2)
#define TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL 1 // Using channel 1 makes tone() independent of receiving timer -> No need to stop receiving timer.
void tone(uint8_t aPinNumber, unsigned int aFrequency){
ledcAttachPin(aPinNumber, TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL);
ledcWriteTone(TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL, aFrequency);
}
void tone(uint8_t aPinNumber, unsigned int aFrequency, unsigned long aDuration){
ledcAttachPin(aPinNumber, TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL);
ledcWriteTone(TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL, aFrequency);
delay(aDuration);
ledcWriteTone(TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL, 0);
}
void noTone(uint8_t aPinNumber){
ledcWriteTone(TONE_LEDC_CHANNEL, 0);
}
#endif // ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION <= ESP_ARDUINO_VERSION_VAL(2, 0, 2)
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 15 // D15
#define IR_SEND_PIN 4 // D4
#define TONE_PIN 27 // D27 25 & 26 are DAC0 and 1
#define APPLICATION_PIN 16 // RX2 pin
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_STM32) || defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_STM32F1) // BluePill
// Timer 3 blocks PA6, PA7, PB0, PB1 for use by Servo or tone()
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN PA6
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN_STRING "PA6"
#define IR_SEND_PIN PA7
#define IR_SEND_PIN_STRING "PA7"
#define TONE_PIN PA3
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN PA5
#define APPLICATION_PIN PA2
#define APPLICATION_PIN_STRING "PA2"
# if defined(ARDUINO_GENERIC_STM32F103C) || defined(ARDUINO_BLUEPILL_F103C8)
// BluePill LED is active low
#define FEEDBACK_LED_IS_ACTIVE_LOW
# endif
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_APOLLO3) // Sparkfun Apollo boards
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 11
#define IR_SEND_PIN 12
#define TONE_PIN 5
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_MBED) && defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_MBED_NANO) // Arduino Nano 33 BLE and Arduino Nano Connect layout for MBED
// Must be before ARDUINO_ARCH_RP2040, since it is the layout for the MBED core of Arduino Nano Connect
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 3 // GPIO15 Start with pin 3 since pin 2|GPIO25 is connected to LED on Pi pico
#define IR_SEND_PIN 4 // GPIO16
#define TONE_PIN 5
#define APPLICATION_PIN 6
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 7 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 8
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_RP2040) // Arduino Nano Connect, Pi Pico with arduino-pico core https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 15 // GPIO15 to be compatible with the Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect (pin3)
#define IR_SEND_PIN 16 // GPIO16
#define TONE_PIN 17
#define APPLICATION_PIN 18
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 19 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 20
// If you program the Nano RP2040 Connect with this core, then you must redefine LED_BUILTIN
// and use the external reset with 1 kOhm to ground to enter UF2 mode
#undef LED_BUILTIN
#define LED_BUILTIN 6
#elif defined(PARTICLE) // !!!UNTESTED!!!
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN A4
#define IR_SEND_PIN A5 // Particle supports multiple pins
#define LED_BUILTIN D7
/*
* 4 times the same (default) layout for easy adaption in the future
*/
#elif defined(TEENSYDUINO) // Teensy 2.0 is handled at default for ATmega328 like on Uno, Nano, Leonardo etc.
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_MBED) // Arduino Nano 33 BLE
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD) || defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAM)
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
#if !defined(ARDUINO_SAMD_ADAFRUIT) && !defined(ARDUINO_SEEED_XIAO_M0)
// On the Zero and others we switch explicitly to SerialUSB
#define Serial SerialUSB
#endif
// Definitions for the Chinese SAMD21 M0-Mini clone, which has no led connected to D13/PA17.
// Attention!!! D2 and D4 are swapped on these boards!!!
// If you connect the LED, it is on pin 24/PB11. In this case activate the next two lines.
//#undef LED_BUILTIN
//#define LED_BUILTIN 24 // PB11
// As an alternative you can choose pin 25, it is the RX-LED pin (PB03), but active low.In this case activate the next 3 lines.
//#undef LED_BUILTIN
//#define LED_BUILTIN 25 // PB03
//#define FEEDBACK_LED_IS_ACTIVE_LOW // The RX LED on the M0-Mini is active LOW
#elif defined (NRF51) // BBC micro:bit
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define APPLICATION_PIN 1
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 4
#define tone(...) void() // no tone() available
#define noTone(a) void()
#define TONE_PIN 42 // Dummy for examples using it
#else
#warning Board / CPU is not detected using pre-processor symbols -> using default values, which may not fit. Please extend PinDefinitionsAndMore.h.
// Default valued for unidentified boards
#define IR_RECEIVE_PIN 2
#define IR_SEND_PIN 3
#define TONE_PIN 4
#define APPLICATION_PIN 5
#define ALTERNATIVE_IR_FEEDBACK_LED_PIN 6 // E.g. used for examples which use LED_BUILDIN for example output.
#define _IR_TIMING_TEST_PIN 7
#endif // defined(ESP8266)
#if defined(ESP32) || defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_RP2040) || defined(PARTICLE) || defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_MBED)
#define SEND_PWM_BY_TIMER // We do not have pin restrictions for this CPU's, so lets use the hardware PWM for send carrier signal generation
#else
# if defined(SEND_PWM_BY_TIMER)
#undef IR_SEND_PIN // SendPin is determined by timer! This avoids warnings in IRremote.hpp and IRTimer.hpp
# endif
#endif
#if !defined (FLASHEND)
#define FLASHEND 0xFFFF // Dummy value for platforms where FLASHEND is not defined
#endif
/*
* Helper macro for getting a macro definition as string
*/
#if !defined(STR_HELPER)
#define STR_HELPER(x) #x
#define STR(x) STR_HELPER(x)
#endif
Select the Arduino Nano
For the PinDefinitionsAndMore.h you have to create a new tab and paste the code above to upload the IR_transponder.ino because the new version of the IRRemote library requires this file now.
Now you can put the IR transmitter on your car and it will count a lap when you pass through the gate.
See how i did it for my car over here.
You can check if the IR LED is working correctly by opening your phone camera to see the LED blinking.
How to connect the wires
Wiring Diagram Overview:
Let’s break down the wiring based on the schematic provided.
Servo:
- Servo SIG (Orange Wire): Pin 18
- VCC (Red Wire): 5V
- GND (Black Wire): GND
ESC:
- ESC SIG (White Wire): Pin 15
- VCC (Red Wire): 5V
- GND (Black Wire): GND
Power:
Connect your ESP32 to 5V and GND to power it.